Swift笔记 - 14.字面量、模式、条件编译、日志、API可用性、程序入口、Swift与OC互调
Swift笔记 - 14.字面量、模式、条件编译、日志、API可用性、程序入口、Swift与OC互调
字面量
var age = 10
var isRed = false
var name = "Jack"
-
上面代码中的
10、false、"Jack"就是字面量 -
常见字面量的默认类型
public typealias IntegerLiteralType = Int
public typealias FloatLiteralType = Double
public typealias BooleanLiteralType = Bool
public typealias StringLiteralType = String
//可以通过typealias修改字面量的默认类型
typealias FloatLiteralType = Float
typealias IntegerLiteralType = UInt8
var age = 10 // UInt8
var height = 1.68 // Float
- Swift自带的绝大部分类型,都支持直接通过字面量进行初始化
Bool、Int、Float、Double、String、Array、Dictionary、Set、Optional等
字面量协议
- Swift自带类型之所以能够通过字面量初始化,是因为它们遵守了对应的协议
Bool: ExpressibleByBooleanLiteralInt : ExpressibleByIntegerLiteralFloat, Double : ExpressibleByIntegerLiteral、ExpressibleByFloatLiteralDictionary : ExpressibleByDictionaryLiteralString : ExpressibleByStringLiteralArray, Set : ExpressibleByArrayLiteralOptional : ExpressibleByNilLiteral
var b: Bool = false // ExpressibleByBooleanLiteral
var i: Int = 10 // ExpressibleByIntegerLiteral
var f0: Float = 10 // ExpressibleByIntegerLiteral
var f1: Float = 10.0 // ExpressibleByFloatLiteral
var d0: Double = 10 // ExpressibleByIntegerLiteral
var d1: Double = 10.0 // ExpressibleByFloatLiteral
var s: String = "jack" // ExpressibleByStringLiteral
var arr: Array = [1, 2, 3] // ExpressibleByArrayLiteral
var set: Set = [1, 2, 3] // ExpressibleByArrayLiteral
var dict: Dictionary = ["jack" : 60] // ExpressibleByDictionaryLiteral
var o: Optional<Int> = nil // ExpressibleByNilLiteral
字面量协议的应用
extension Int : ExpressibleByBooleanLiteral {
public init (booleanLiteral value: Bool) { self = value ? 1 : 0 }
}
var num: Int = true
print(num) // 1
- 有点类似于C++中的转换构造函数
class Student : ExpressibleByIntegerLiteral, ExpressibleByFloatLiteral, ExpressibleByStringLiteral, CustomStringConvertible {
var name: String =
var score: Double = 0
required init(floatLiteral value: Double) { self.score = value }
required init (integerLiteral value: Int) { self.score = Double(value) }
required init(stringLiteral value: String) { self.name = value }
required init(unicodeScalarLiteral value: String) { self.name = value }
required init(extendedGraphemeClusterLiteral value: String) { self.name = value }
var description: String { "name=\(name), score=\(score)" }
}
var stu: Student = 90
print(stu) // name=, score=90.0
stu = 98.5
print(stu) // name=, score=98.5
stu = "Jack"
print(stu) // name=Jack, score=0.0
struct Point {
var X = 0.0, y = 0.0
}
extension Point : ExpressibleByArrayLiteral, ExpressibleByDictionaryLiteral {
init (arrayLiteral elements: Double...) {
guard elements.count> 0 else { return }
self.x = elements[0]
guard elements.count > 1 else { return }
self.y = elements[1]
}
init(dictionaryLiteral elements: (String, Double)...) {
for (k, v) in elements {
if k == "x" { self.x = v }
else if k == "y" { self.y = v }
}
}
}
var p: Point = [10.5, 20.5]
print(p) // Point (x: 10.5, y: 20.5)
p = ["x' : 11, "y" : 22]
print(p) // Point(x: 11.0, y: 22.0)
Swift 里的模式
- 什么是模式?
- 模式是用于匹配的规则,比如
switch的case、捕捉错误的catch.if\guard\while\for语句的条件等
- 模式是用于匹配的规则,比如
- Swift中的模式有
- 通配符模式(Wildcard Pattern)
- 标识符模式(Identifier Pattern)
- 值绑定模式(Value-Binding Pattern)
- 元组模式(Tuple Pattern)
- 枚举Case模式(Enumeration Case Pattern)
- 可选模式(Optional Pattern)
- 类型转换模式(Type-Casting Pattern)
通配符模式
_匹配任何值_?匹配非nil值
enum Life {
case human (name: String, age: Int?)
case animal(name: String, age: Int?)
}
func check( life: Life)
switch life {
case .human(let name, _):
print ("human", name)
case .animal(let name, ?): //age非空才匹配
print ("animal", name)
default:
print ("other")
}
}
check(.human(name: "Rose", age: 20)) // human Rose
check(.human(name: "Jack", age: nil)) // human Jack
check(.animal(name: "Dog", age: 5)) // animal Dog
check(.animal(name:"Cat", age: nil)) // other
var num: Int? = 10
switch num {
case let v?:
print(v)
case nil:
print("nil")
}
// output:
// false
// Program ended with exit code:
标识符模式
- 给对应的变量、常量名赋值
var age = 10
let name = "jack"
- 值绑定模式
let point = (3, 2)
switch point {
case let (x, y) :
print("The point is at (\(x), \(y)).")
}
- 元组模式
let points = [(0, 0), (1, 0), (2, 0)]
for (x, _) in points {
print(x)
}
let name: String? = "jack"
let age = 18
let info: Any = [1, 2]
switch (name, age, info) {
case (?, _, _ as String):
print ("case")
default:
print ("default")
}
// default
var scores = ["jack" : 98, "rose" : 100, "kate" : 86]
for (name, score) in scores {
print(name, score)
}
-
枚举Case模式
if case语句等价于只有1个case的switch语句
let age = 2
//原来的写法
if age >= 0 && age <= 9 {
print("[0, 9]")
}
// 枚举用例模式
if case 0...9 = age {
print ("[0, 9]")
}
guard case 0...9 = age else { return }
print ("[0, 9]")
switch age {
case 0...9: print("[0, 9]")
default: break
}
let ages: (Int?] = [2, 3, nil, 5]
for case nil in ages {
print("有nil值")
break
} // 有nil值
let points = [(1, 0), (2, 1), (3, 0)]
for case let (x, 0) in points {
print(x)
} // 1 3
- 可选模式
let age: Int? = 42
if case .some (let x) = age { print(x) }
if case let x? = age { print(x) }
let ages: [Int?] = [nil, 2, 3, nil, 5]
for case let age? in ages {
print (age)
} // 2 3 5
let ages: [Int?] = [nil, 2, 3, nil, 5]
for item in ages {
if let age = item {
print (age)
}
//跟上面的for,效果是等价的
func check(_ num: Int?) {
switch num {
case 2?: print("2")
case 4?: print("4")
case 6?: print("6")
case _?: print("other")
case _: print ("nil")
}
}
check(4) // 4
check(8) // other
check(nil) // nil
以下两种写法等价:
var age: Int? = 10
switch age {
case let x?:
print(x)
case nil:
print ("nil")
}
switch age {
case .some(let x):
print(x)
case .none:
print("nil")
}
- 类型转换模式
let num: Any = 6
switch num {
case is Int:
//编译器依然认为nlm是Any类型
print ("is Int", num)
//case let n as Int:
// print ("as Int", n + 1)
default:
break
}
class Animal ( func eat() { print(type(of: self), "eat") }
class Dog : Animal { func run() { print(type(of: self), "run")
class Cat : Animal { func jump() { print (type(of: self), "jump") }
func check( animal: Animal) {
switch animal (
case let dog as Dog:
dog.eat()
dog.run()
case is Cat: //is只是判斷没有转换
animal.eat() //只能调Animal的eat
default: break
}
}
// Dog eat
// Dog run
check(Dog())
// Cat eat
check(Cat0))
- 表达式模式
- 表达式模式用在
case中
- 表达式模式用在
let point = (1, 2)
switch point {
case (0, 0):
print("(0, 0) is at the origin.")
case (-2...2, -2...2):
print(" (\(point.0), \(point.1)) is near the drigin.")
default:
print ("The point is at (\(point.0), \(point.1)).")
}
// (1, 2) is near the origin
- 自定义表达式模式
- 可以通过重载运算符,自定叉表达式模式的匹配规则
struct Student { // 重载 ~= 运算符
var score = 0, name = ""
static func ~= (pattern: Int, value: Student) -> Bool { value.score >= pattern }
static func ~= (pattern: ClosedRange<Int>, value: Student) -> Bool { pattern.contains (value.score) }
static func
~= (pattern: Range<Int>, value: Student) -> Bool { pattern.contains (value.score) }
}
var stu = Student(score: 75, name: "Jack")
switch stu {
case 100: print(">= 100")
case 90: print(">= 90")
case 80..<90: print("[80, 90)")
case 60...79: print("[60, 79]")
case 0: print(">= 0")
default: break
} // [60, 79]
if case 60 = stu {
print(">= 60")
} // = 60
var info = (Student(score:70, name: "Jack"), "及格")
switch info {
case let (60, text): print(text)
default: break
} //及格
extension String {
static func ~= (pattern: (String) -> Bool, value: String)
-> Bool
pattern(value)
}
}
func hasPrefix(_ s: String) -> ((String) -> Bool) { ( $0.hasPrefix(s) }
func hasSuffix(_ s: String) -> ((String) -> Bool) { { $0.hasSuffix(s) }
//以上两行 等价于下面的函数
//func hasPrefix(_ prefix: String) -> ((String) -> Bool) {
// return { (str: String) -> Bool in
// str.hasPrefix(prefix)
// }
//}
//var fn = hasPrefix("21")
//print(fn("123455"))
var str = "jack"
switch str {
case hasPrefix("j"), hasSuffix("k"):
print("以j开头,以k结尾")
default: break
} //以开头,以k结尾
func isEven(_ i: Int) -> Bool { 1 % 2== 0 }
func isOdd(_ i: Int) -> Bool { 1 % 2 != a }
extension Int {
static func ~=I(pattern: (Int) -> Bool, value: Int) -> Bool (
pattern(value)
}
}
var age = 9
switch age {
case isEven:
print ("偶数")
case isOdd:
print("奇数")
default:
print ("其他")
}
prefix operator ~>
prefix operator ~>=
prefix operator ~
prefix operator ~<=
prefix func ~> (_ i: Int) -> ((Int) -> Bool) { { $0 > i } }
prefix func ~>= (_ i: Int) -> ((Int) -> Bool) { { $0 >= i }
prefix func ~ (_ i: Int) -> ((Int) -> Bool) { { $0 < i } }
prefix func ~<= (_ i: Int) -> ((Int) -> Bool) { { $0 <= i } }
var age = 9
switch age {
case ~>=0, ~<=10:
print("[0, 10]")
case ~>10, ~<20:
print("(10, 20)")
default: break
} // [0, 101
- where在模式匹配中应用
- 可以使用
where为模式匹配增加匹配条件
- 可以使用
var data = (10, "Jack")
switch data {
case let (age, _) where age > 10:
print(data. 1, "age>10")
case let (age, _) where age > 0:
print(data. 1, "age>0")
default: break
}
var ages = [10, 20, 44, 23, 55]
for age in ages where age > 30 {
print (age)
} // 44 55
protocol Stackable { associatedtype Element }
protocol Container {
associatedtype Stack : Stackable where Stack.Element : Equatable
}
func equal<S1: Stackable, S2: Stackable>(_ s1: S1, _ $2: S2) -> Bool where S1.Element == S2.Element, S1.Element : Hashable (
return false
}
extension Container where Self.Stack.Element : Hashable { }
条件编译
//操作系统:macOS\iOS\tvOS\watchOS\Linux\Android\Windows\FreeBsD
#if os(macOS) || os(iOS)
/1 CPU架构: i386\x86_64\arm\arm64
#elseif arch(x86 64) || arch(arm64)
//swift版本
#elseif swift(<5) && swift(>=3)
//模拟器
#elseif targetEnvironment(simulator)
//可以导入某模块
#elseif canImport(Foundation)
#else
#endif
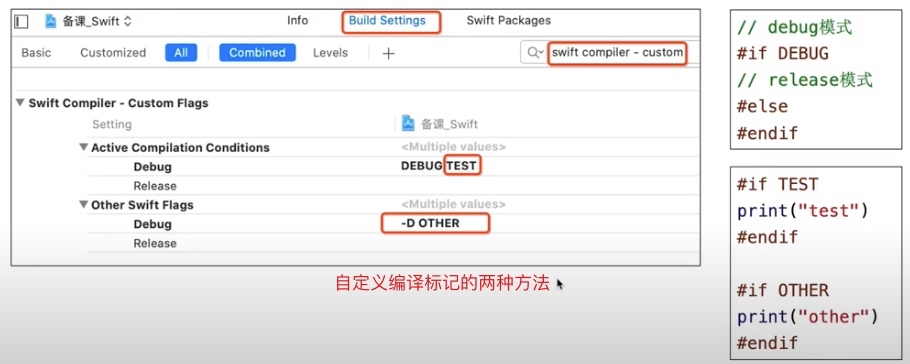
打印日志
func log<T>(_ msg: T,
file: NSString = #file,
line: Int = #line,
fn: String = #function) {
#if DEBUG
let prefix = "\(file. lastPathComponent)_\(line)_\(fn): "
print (prefix, msg)
#endif
系统版本
if #available(iOS 10, macOS 10.12,*) {
//对于i0S平台,只在i0S10及以上版本执行
//对于macOS平台,只在macOS 10.12及以上版本执行
//最后的*表示在其他所有平台都执行
API可用性
@available(iOS 10, macOS 10.15, *)
class Person (
struct Student {
@available(*, unavailable, renamed: "study")
func study_() {}
func study() {}
@available(i0S, deprecated: 11)
@available(macOS, deprecated: 10.12)
func run() {}
}
自定义iOS程序入口
- 在
AppDelegate上面默认有个@UIApplicationMain标记,这表示- 编译器自动生成入口代码(
main函数代码),自动设置AppDelegate为APP的代理
- 编译器自动生成入口代码(
- 也可以删掉
@UIApplicationMain,自定义入口代码:新建一个main.swift文件
// main.swift
// Test iOS
// Created by MJ Lee on 2019/7/22.
// Copyright © 2019 MJ Lee. All rights reserved.
import UIKit
class XXApplication: UIApplication {}
UIApplicationMain(CommandLine.argc,
CommandLine.unsafeArgv,
NSStringFromClass(XXApplication.self),
NSStringFromClass(AppDelegate.self))
Swift调用OC
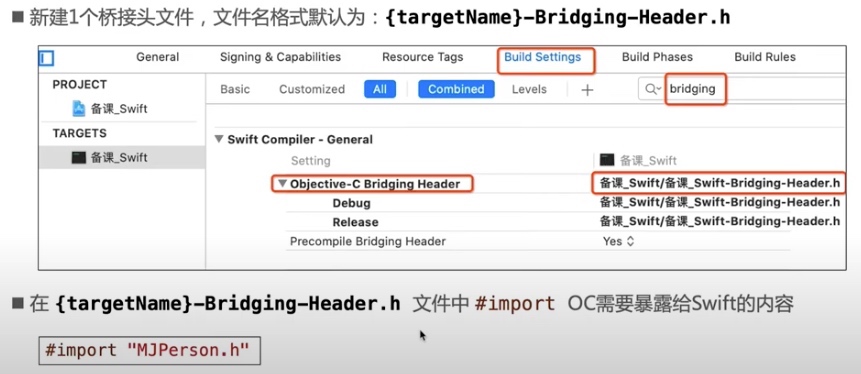
- 新建1个桥接头文件,文件名格式默认为:
{targetName}-Bridging-Header.h - 在
{targetName}-Bridging-Header.h文件中#importOC需要暴露给Swift的内容#import "Person.h'
- 在Swift中修改C函数名
- 如果C语言暴露给Swift的西数名跟Swift中的其他两数名冲突了
- 可以在Swift中使用
@_silgen_name修改C函数名
- 可以在Swift中使用
- 如果C语言暴露给Swift的西数名跟Swift中的其他两数名冲突了
//C语言
int sum(int a, int b) {
return a + b;
}
// Swift
@silgen_name("sum") func swift_sum(_ v1: Int32, _ v2: Int32) -> Int32
print(swift_sum(10, 20)) // 30
print(sum(10, 20)) // 30
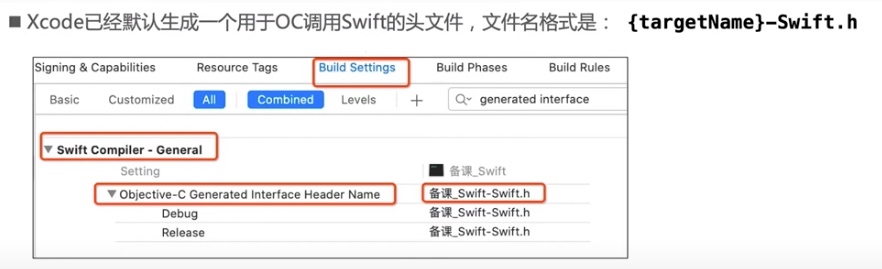
OC调用Swift
- xcode已经默认生成一个用于C调用Swift的头文件,文件名格式是:
{targetName了-Swift.h
import Foundation
@objcMembers class Car: NSObject (
var price: Double
var band: String
init (price: Double, band: String) {
self.price = price
self.band = band
}
func run() { print(price, band, "run") }
static func run() { print("Car run") }
}
extension car {
@objc(exec:v2: )
func test() { print(price, band, "test") }
}
- Swift暴露给OC的类最终继承自
NSObject - 使用
@objc修饰需要暴露给OC的成员 - 使用
@objcMembers修饰类- 代表默认所有成员都会暴露给OC(包括扩展中定义的成员)
- 最终是否成功暴露,还需要考虑成员自身的访问级别
- 可以通过
@objc重命名Swift暴露给OC的符号名(类名、厲性名、函数名等)
@obic(XXCar)
@objcMembers class Car: NSObject
var price: Double
@objc(name)
var band: String
init(price: Double, band: String) (
self.price = price
self.band = band
}
@objc(drive)
func run() { print(price, band, "run") }
static func run() { print ("Car run") }
}
extension Car {
@objc(exec:v2: )
func test() { print (price, band, "test"}
}
XXCar *c = ([XXCar alloc] initWithPrice: 10.5 band: @"BMW"] ;
c.name = @'Bently";
c.price = 108.5;
[c drivel; // 108.5 Bently run
[c exec: 10 v2:20]; // 108.5 Bently test
[XXCar run]; // Car run