计数排序
计数排序
计数排序是通过计算数组中每个唯个元素的出现次数来对数组的元素进行排序。把计数存储在辅助数组中,通过将计数映射为辅助数组的索引来完成排序。
其原理是构造一个计数数组,将原数组的元素值映射为计数数组的索引,因索引自然有序,只要迭代取出计数不为零的索引,构造到新数组即是排好序的。

计数排序的工作流程
-
在给定的数组中找出最大值
max;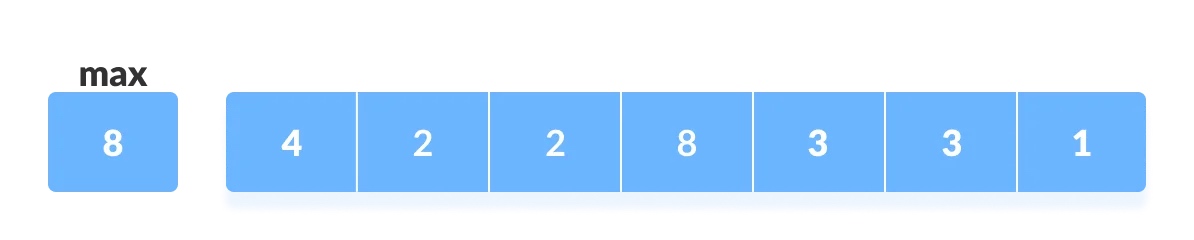
-
创建一个大小为
max+1、所有元素值为0的辅助数组Count array;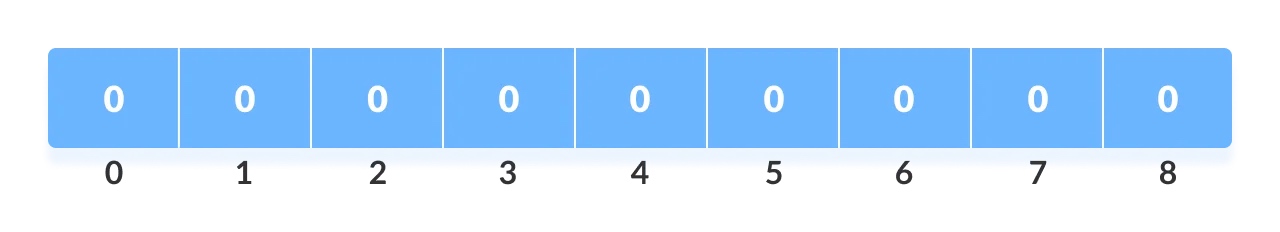
-
将每个元素的计数存储在辅助数组
Count arrary中各自的索引处;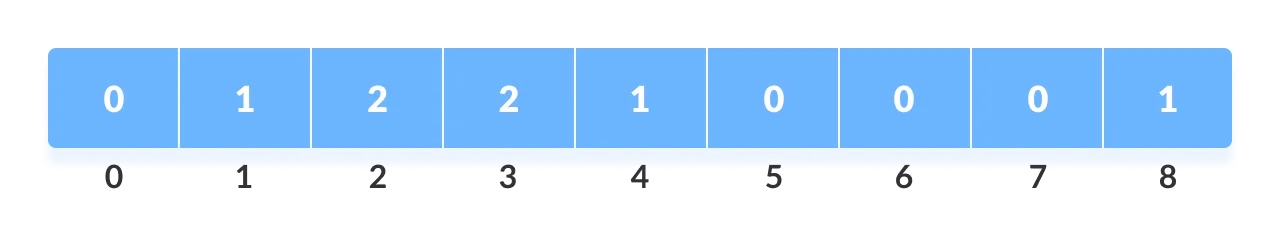
- 存储辅助数组
Count array元素的累积和(也就是各元素的前缀和)数组Cumulative count,这样做是为了便于将元素存放到排序数组的正确索引中;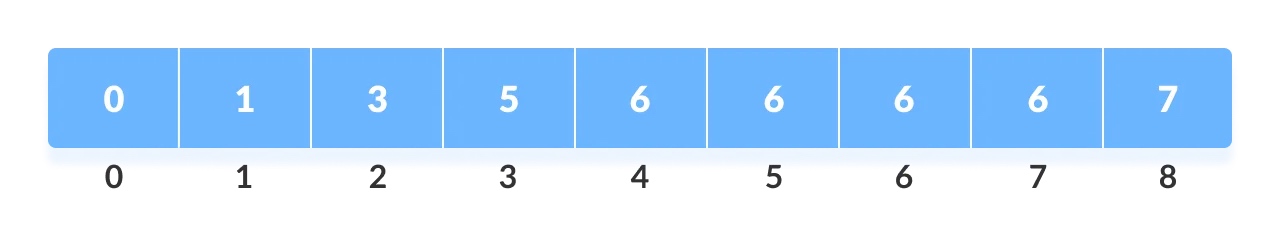
前缀和数据代表了对应的索引元素被按序排在了排序数组的哪一位上。
-
找出原数组中每个元素在计数数组
Count array中的索引,这个找索引的过程借助于前缀和数组Cumulative count来实现。过程如下图: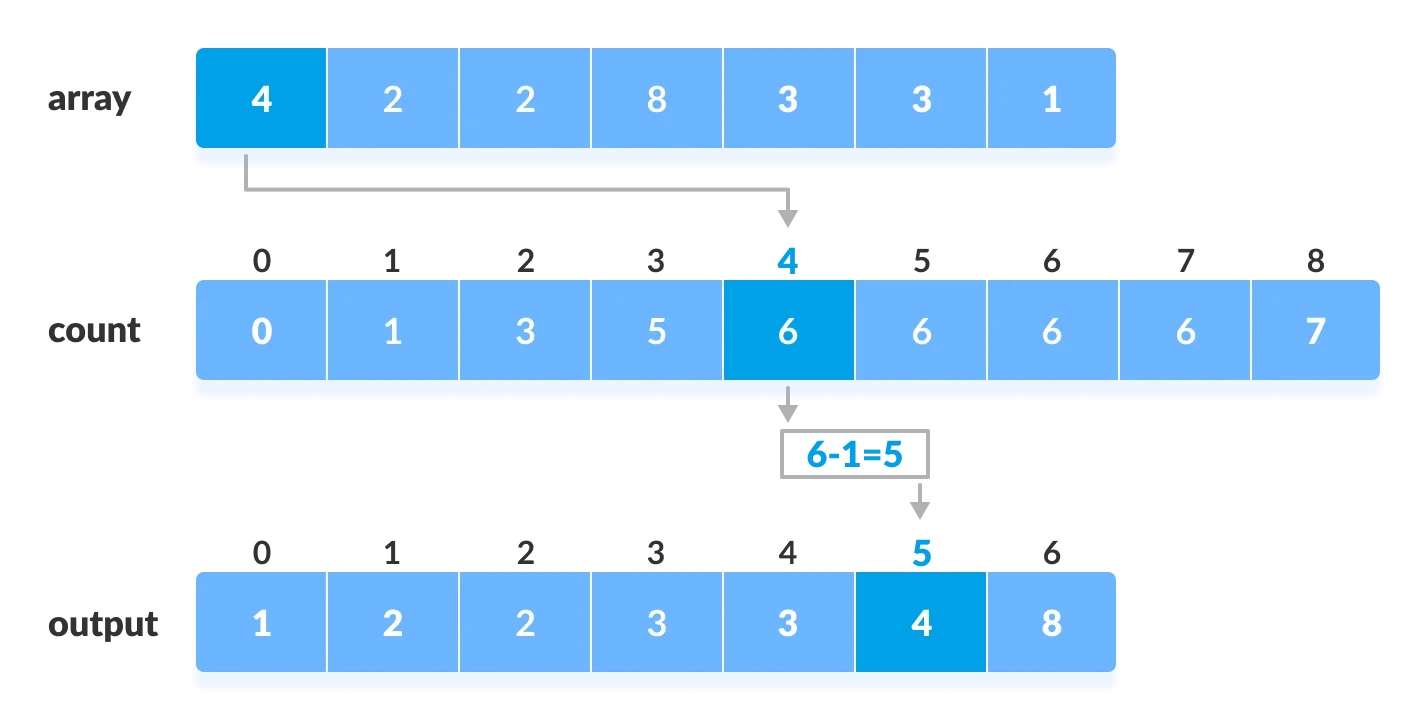
- 将每个元素放在正确的位置后,将其在
Cumulative count中的计数减1。
复杂度
|Time Complexity|| |—|—| |Best | O(n+k) | |Worst | O(n+k) | |Average | O(n+k) | |Space Complexity | O(max) | |Stability | Yes |
代码实现
Swift实现
import Foundation
//计数排序的原理:构造一个计数数组,将原数组的元素值映射为计数数组的索引,因索引自然有序,只要迭代取出计数不为零的索引,构造到新数组即是排好序的
func countSort(array:inout [Int]) {
//获得数组中的最大值
let max = array.max() ?? 0
//定义一个大小为(max+1)的计数数组
var count = [Int](https://luowei.github.io/list/repeating: 0, count: max+1)
//先算每个元素(索引位置)的计数,得到元数的计数数组。以原数组值为索引,在count中存储这个值在原数组中出现的计数
for i in 0 ..< array.count {
count[array[i]] += 1
}
// // ---- 方式一 ----
// var index = 0
// for i in 0 ..< count.count {
// while count[i] > 0 && index < array.count {
// //重排array
// array[index] = i
// index += 1
//
// count[i] -= 1 //累加数减1
// }
// }
// // ---------------
// ---- 方式二 ----
//再算每个元素(索引位置)的计数前缀累积和,得到一个索引计数的前缀和数组
for i in 1 ..< count.count {
count[i] += count[i - 1]
}
//print("== cosum:\(count)")
//定义一个输出数组
var output = [Int](https://luowei.github.io/list/repeating: 0, count: array.count)
//count数组中的某个索引的累积和,代表这个索引对应元素应该在原数组中排在什么位置
//所以遍历原数组中每个元素,根据这个元素在count数组中的累积和,得出它应该排在数组中的 count[array[i]] - 1
//for i in 0 ..< array.count {
for i in stride(from: array.count - 1, through:0, by: -1) { //注意这里要倒序遍历,不然多次调用此排序方法顺序就不对了
output[count[array[i]] - 1] = array[i]
count[array[i]] -= 1
}
//将outpu拷贝到原数组
for i in 0 ..< array.count {
array[i] = output[i]
}
// ---------------
}
//打印
func printCountSort(_ array:inout [Int]){
//var array:[Float] = [3, 2, 5, 7, 1, 5, 4, 8, 11, 0]
countSort(array: &array)
print(array)
}
var arr:[Int] = [3, 2, 5, 7, 1, 5, 4, 8, 11, 0]
printCountSort(&arr)
Python实现
# Counting sort in Python programming
def countingSort(array):
size = len(array)
output = [0] * size
# Initialize count array
count = [0] * 10
# Store the count of each elements in count array
for i in range(0, size):
count[array[i]] += 1
# Store the cummulative count
for i in range(1, 10):
count[i] += count[i - 1]
# Find the index of each element of the original array in count array
# place the elements in output array
i = size - 1
while i >= 0:
output[count[array[i]] - 1] = array[i]
count[array[i]] -= 1
i -= 1
# Copy the sorted elements into original array
for i in range(0, size):
array[i] = output[i]
data = [4, 2, 2, 8, 3, 3, 1]
countingSort(data)
print("Sorted Array in Ascending Order: ")
print(data)
Java实现
// Counting sort in Java programming
import java.util.Arrays;
class CountingSort {
void countSort(int array[], int size) {
int[] output = new int[size + 1];
// Find the largest element of the array
int max = array[0];
for (int i = 1; i < size; i++) {
if (array[i] > max)
max = array[i];
}
int[] count = new int[max + 1];
// Initialize count array with all zeros.
for (int i = 0; i < max; ++i) {
count[i] = 0;
}
// Store the count of each element
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {
count[array[i]]++;
}
// Store the cummulative count of each array
for (int i = 1; i <= max; i++) {
count[i] += count[i - 1];
}
// Find the index of each element of the original array in count array, and
// place the elements in output array
for (int i = size - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
output[count[array[i]] - 1] = array[i];
count[array[i]]--;
}
// Copy the sorted elements into original array
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {
array[i] = output[i];
}
}
// Driver code
public static void main(String args[]) {
int[] data = { 4, 2, 2, 8, 3, 3, 1 };
int size = data.length;
CountingSort cs = new CountingSort();
cs.countSort(data, size);
System.out.println("Sorted Array in Ascending Order: ");
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(data));
}
}
C 实现
// Counting sort in C programming
#include <stdio.h>
void countingSort(int array[], int size) {
int output[10];
// Find the largest element of the array
int max = array[0];
for (int i = 1; i < size; i++) {
if (array[i] > max)
max = array[i];
}
// The size of count must be at least (max+1) but
// we cannot declare it as int count(max+1) in C as
// it does not support dynamic memory allocation.
// So, its size is provided statically.
int count[10];
// Initialize count array with all zeros.
for (int i = 0; i <= max; ++i) {
count[i] = 0;
}
// Store the count of each element
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {
count[array[i]]++;
}
// Store the cummulative count of each array
for (int i = 1; i <= max; i++) {
count[i] += count[i - 1];
}
// Find the index of each element of the original array in count array, and
// place the elements in output array
for (int i = size - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
output[count[array[i]] - 1] = array[i];
count[array[i]]--;
}
// Copy the sorted elements into original array
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {
array[i] = output[i];
}
}
// Function to print an array
void printArray(int array[], int size) {
for (int i = 0; i < size; ++i) {
printf("%d ", array[i]);
}
printf("\n");
}
// Driver code
int main() {
int array[] = {4, 2, 2, 8, 3, 3, 1};
int n = sizeof(array) / sizeof(array[0]);
countingSort(array, n);
printArray(array, n);
}
C++ 实现
// Counting sort in C++ programming
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
void countSort(int array[], int size) {
// The size of count must be at least the (max+1) but
// we cannot assign declare it as int count(max+1) in C++ as
// it does not support dynamic memory allocation.
// So, its size is provided statically.
int output[10];
int count[10];
int max = array[0];
// Find the largest element of the array
for (int i = 1; i < size; i++) {
if (array[i] > max)
max = array[i];
}
// Initialize count array with all zeros.
for (int i = 0; i <= max; ++i) {
count[i] = 0;
}
// Store the count of each element
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {
count[array[i]]++;
}
// Store the cummulative count of each array
for (int i = 1; i <= max; i++) {
count[i] += count[i - 1];
}
// Find the index of each element of the original array in count array, and
// place the elements in output array
for (int i = size - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
output[count[array[i]] - 1] = array[i];
count[array[i]]--;
}
// Copy the sorted elements into original array
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {
array[i] = output[i];
}
}
// Function to print an array
void printArray(int array[], int size) {
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++)
cout << array[i] << " ";
cout << endl;
}
// Driver code
int main() {
int array[] = {4, 2, 2, 8, 3, 3, 1};
int n = sizeof(array) / sizeof(array[0]);
countSort(array, n);
printArray(array, n);
}