插入排序
插入排序
插入排序是在每次迭代中将未排序的元素放在合适的位置。插入排序的工作原理与我们在玩纸牌游戏时,对自己手中的牌进行排序过程类似。
我们假设第一张牌已经排序,然后我们选择一张未排序的牌。 如果未排序的牌大于手中的牌,则将其放在右侧,否则放在左侧。以同样的方式,把其他未分类的牌一张张取出并放在正确的位置,完成后即排好序了。

插入排序的工作流程
假设我们要对这个数组排序 
-
先预设第1个元素是排序好,再每后面的元素(也就是第2个元素)作为关键元素,然后与前面排好序的进行比较交换操作;
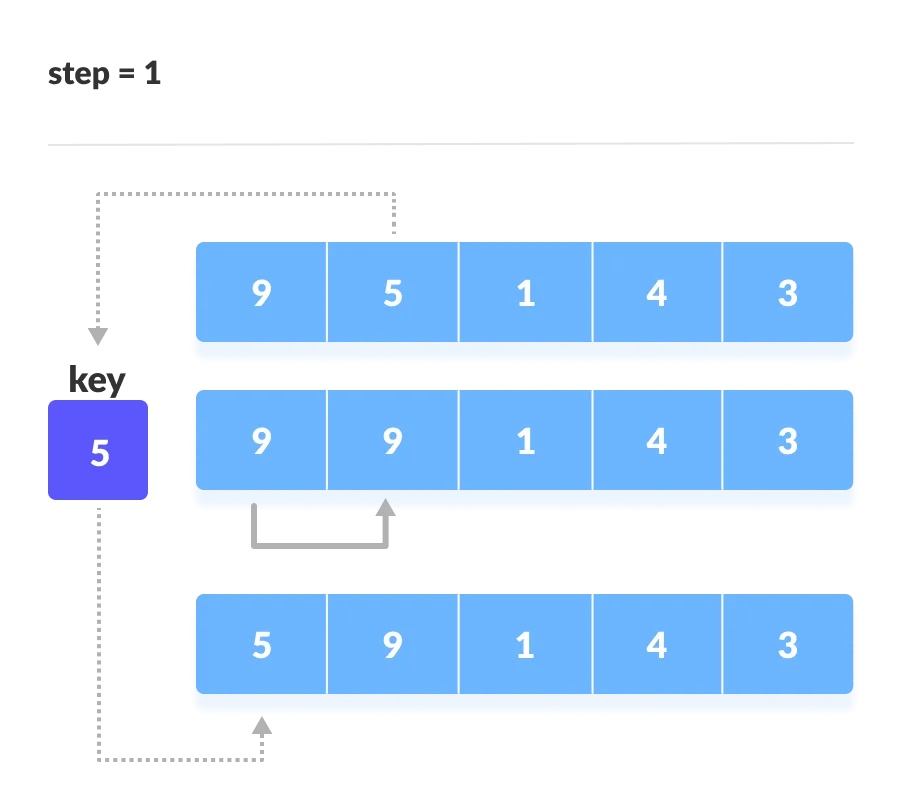
-
然后,从后面未排序的元素(即前面已排好序的后面的元素)中继续拿第1个作为关键元素,与前面的有序列表进行比较交换;
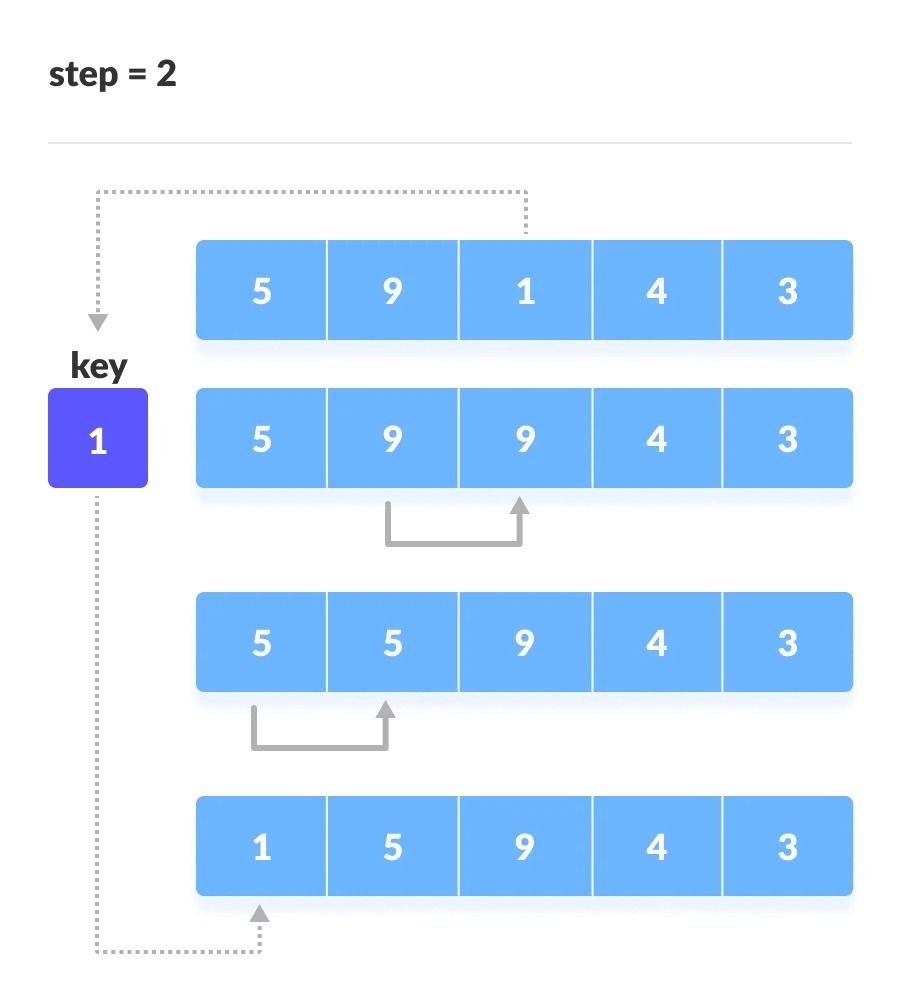
-
对后续的每一轮都做同样的操作,直接最后一个元素;
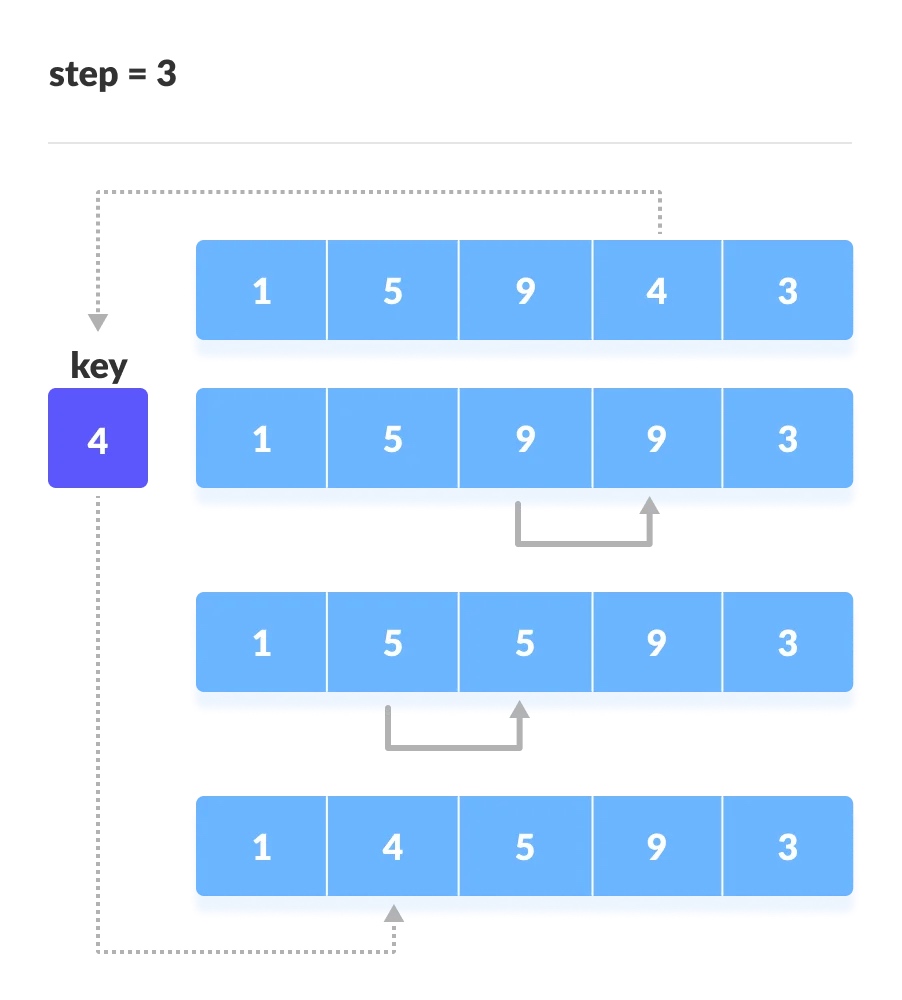
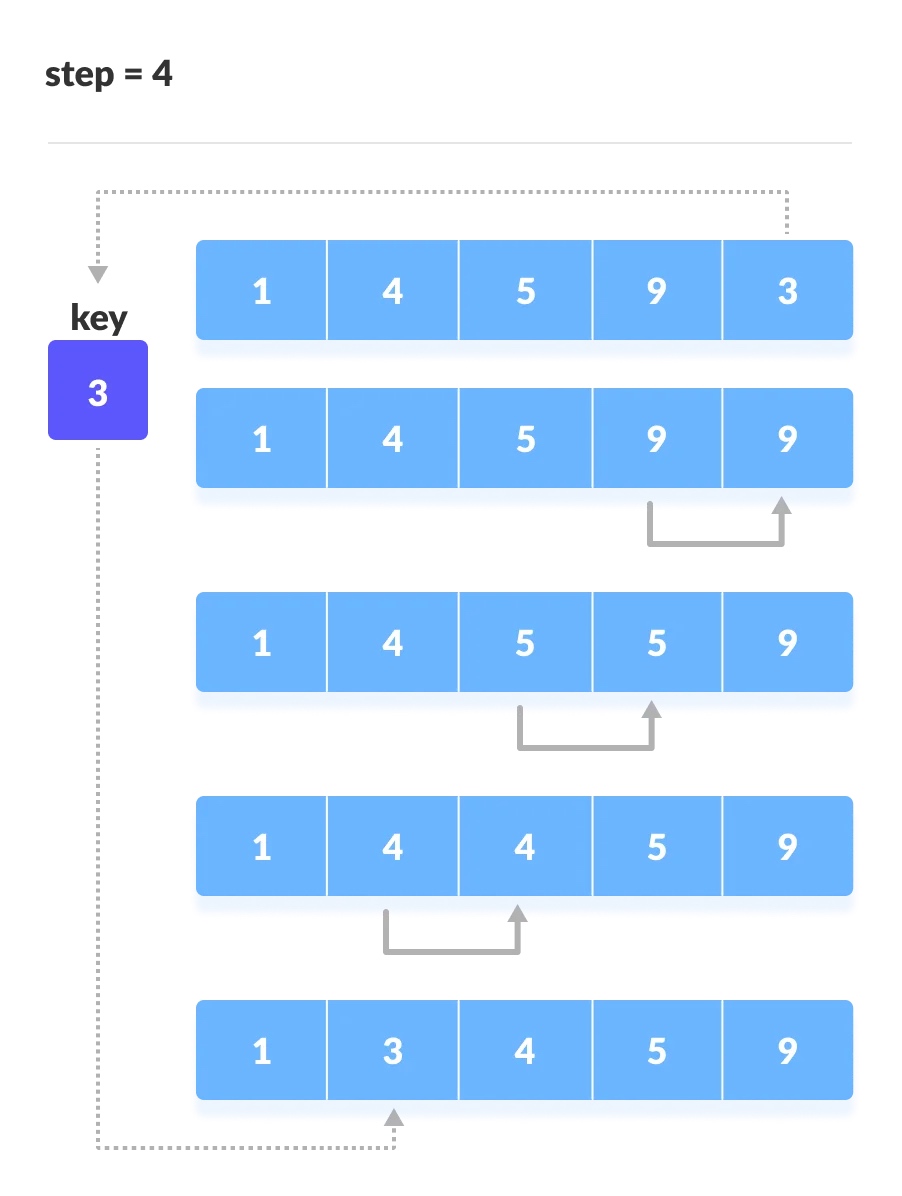
复杂度
|Time Complexity|| |—|—| |Best | O(n) | |Worst | O(n^2) | |Average | O(n^2) | |Space Complexity | O(1) | |Stability | Yes |
代码实现
Swift实现
import Foundation
func insertionSort(array:inout [Int]) {
//先假设第1个元素是已经排好序的,放到左边;我们从右边开始开始遍历,也就是从第2个元素开始
for i in 1 ..< array.count {
//取出第i个作为此轮的关键元素key,将来要把它插入到左边有序列表的正确位置上
let key = array[i]
//定义一个指针j指到左边已排好序的最尾部的元素上,即(i-1)
var j = i - 1
//然后把key与左边的每个元素比较,并利用一个指针j找到可以正确插入的位置
while j >= 0 && key < array[j] {
//因为key < array[j] 说明 key的位置在j的前面;因为key要在j前面插入,所以这里j要往后挪,留出一个空位来
array[j+1] = array[j]
//然后指针j继续往前走
j -= 1
}
//经过前面的while循环判断后,就定位到key要插入的正确位置在指针j所指的后面1个位置,在这个位置插入j即可
array[j+1] = key
}
}
//打印
func printInsertionSort(_ array:inout [Int]){
insertionSort(array: &array)
print(array)
}
var arr:[Int] = [3, 2, 5, 7, 1, 5, 4, 8, 11, 0]
printInsertionSort(&arr)
Python 实现
# Insertion sort in Python
def insertionSort(array):
for step in range(1, len(array)):
key = array[step]
j = step - 1
# Compare key with each element on the left of it until an element smaller than it is found
# For descending order, change key<array[j] to key>array[j].
while j >= 0 and key < array[j]:
array[j + 1] = array[j]
j = j - 1
# Place key at after the element just smaller than it.
array[j + 1] = key
data = [9, 5, 1, 4, 3]
insertionSort(data)
print('Sorted Array in Ascending Order:')
print(data)
Java 实现
// Insertion sort in Java
import java.util.Arrays;
class InsertionSort {
void insertionSort(int array[]) {
int size = array.length;
for (int step = 1; step < size; step++) {
int key = array[step];
int j = step - 1;
// Compare key with each element on the left of it until an element smaller than
// it is found.
// For descending order, change key<array[j] to key>array[j].
while (j >= 0 && key < array[j]) {
array[j + 1] = array[j];
--j;
}
// Place key at after the element just smaller than it.
array[j + 1] = key;
}
}
// Driver code
public static void main(String args[]) {
int[] data = { 9, 5, 1, 4, 3 };
InsertionSort is = new InsertionSort();
is.insertionSort(data);
System.out.println("Sorted Array in Ascending Order: ");
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(data));
}
}
C 实现
// Insertion sort in C
#include <stdio.h>
// Function to print an array
void printArray(int array[], int size) {
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {
printf("%d ", array[i]);
}
printf("\n");
}
void insertionSort(int array[], int size) {
for (int step = 1; step < size; step++) {
int key = array[step];
int j = step - 1;
// Compare key with each element on the left of it until an element smaller than
// it is found.
// For descending order, change key<array[j] to key>array[j].
while (key < array[j] && j >= 0) {
array[j + 1] = array[j];
--j;
}
array[j + 1] = key;
}
}
// Driver code
int main() {
int data[] = {9, 5, 1, 4, 3};
int size = sizeof(data) / sizeof(data[0]);
insertionSort(data, size);
printf("Sorted array in ascending order:\n");
printArray(data, size);
}
C++ 实现
// Insertion sort in C++
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
// Function to print an array
void printArray(int array[], int size) {
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {
cout << array[i] << " ";
}
cout << endl;
}
void insertionSort(int array[], int size) {
for (int step = 1; step < size; step++) {
int key = array[step];
int j = step - 1;
// Compare key with each element on the left of it until an element smaller than
// it is found.
// For descending order, change key<array[j] to key>array[j].
while (key < array[j] && j >= 0) {
array[j + 1] = array[j];
--j;
}
array[j + 1] = key;
}
}
// Driver code
int main() {
int data[] = {9, 5, 1, 4, 3};
int size = sizeof(data) / sizeof(data[0]);
insertionSort(data, size);
cout << "Sorted array in ascending order:\n";
printArray(data, size);
}