选择排序
选择排序
选择排序在每次迭代中从未排序列表中选择最小的元素,并将该元素放在未排序列表的开头。
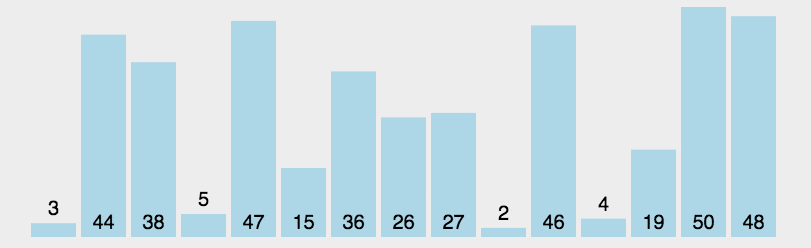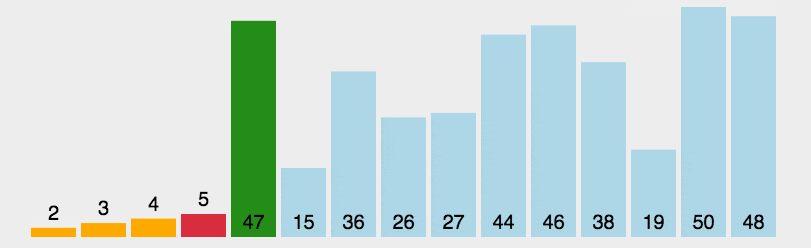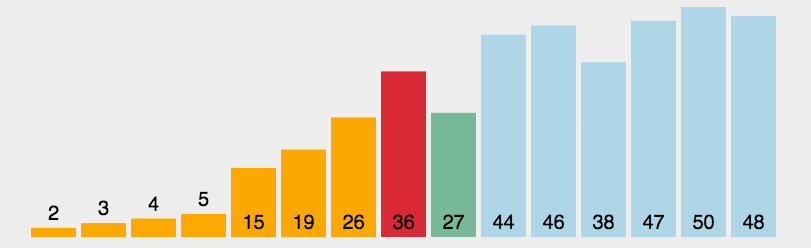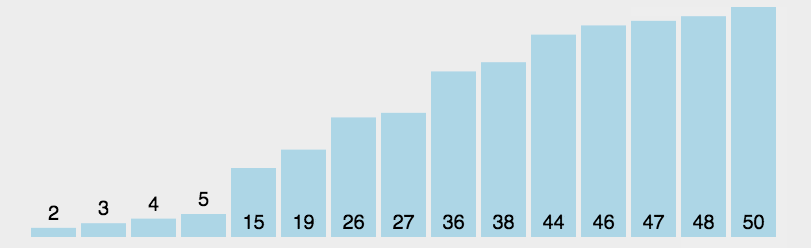
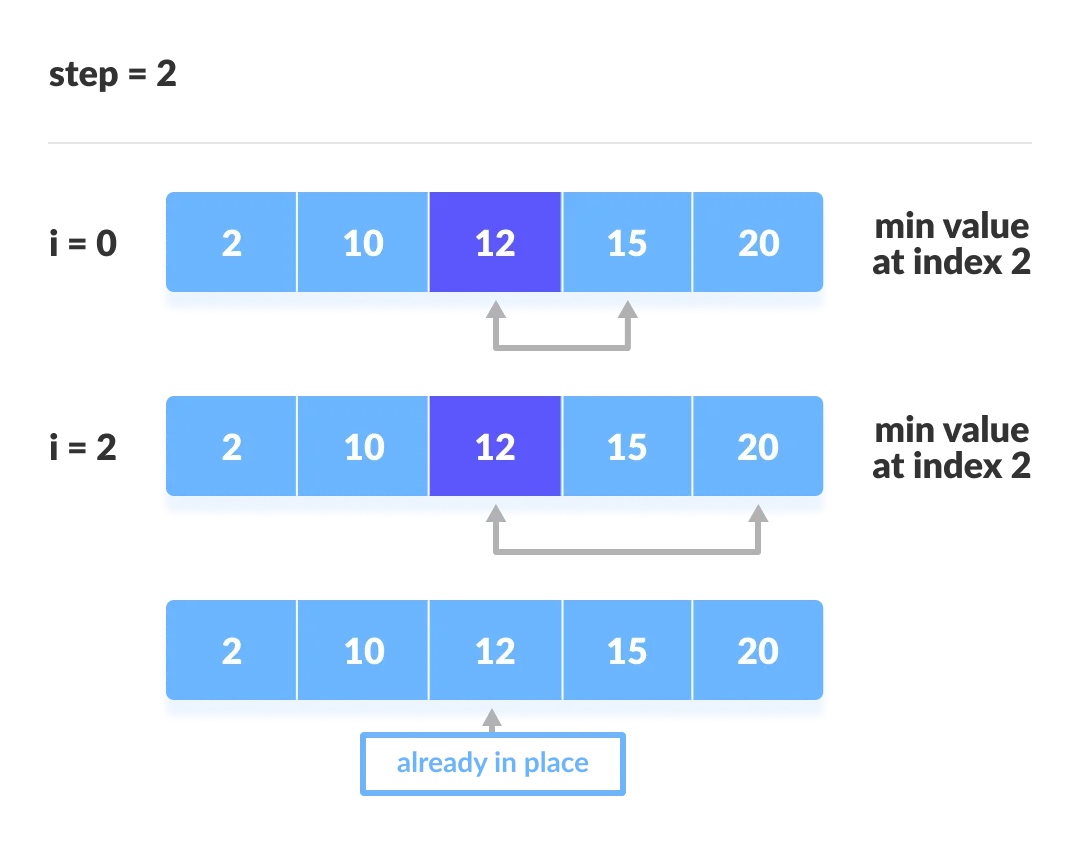
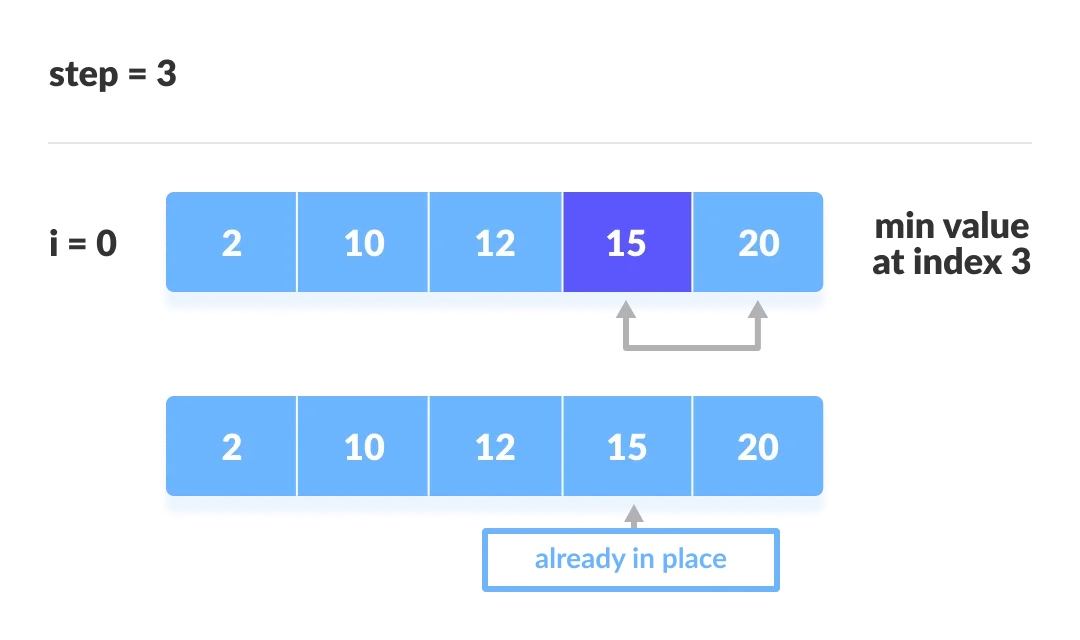
选择排序的工作流程
1. 先假定第一个元素作为最小的元素

2. 迭代依次比较后续相邻元素,找到最小元素
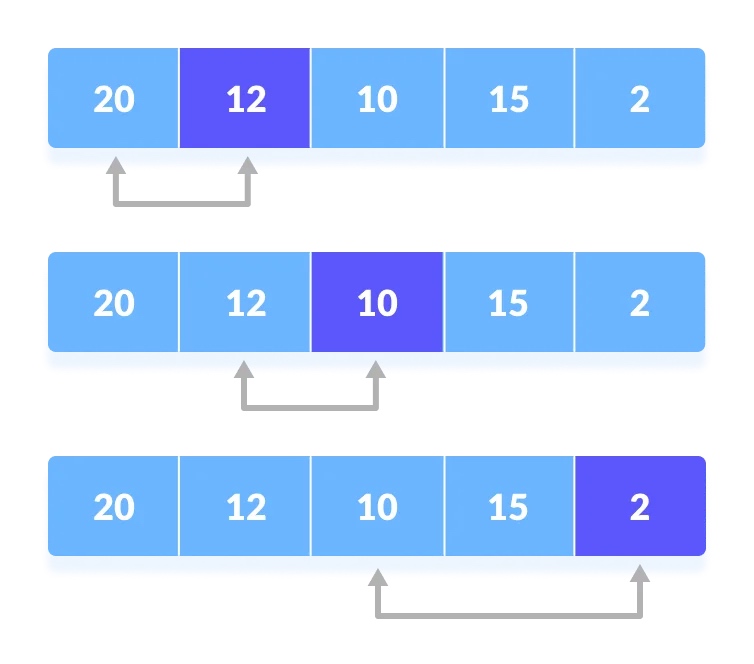
3. 把每一轮迭代找到的最小元素置换到未排序列表的最前面
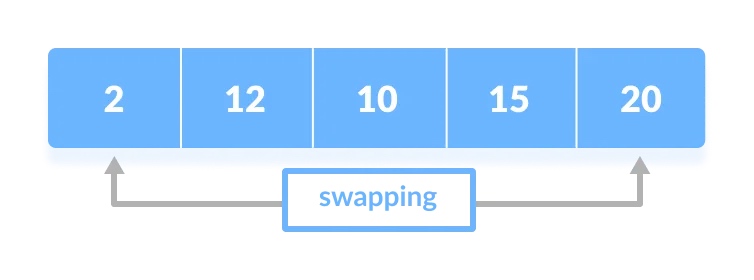
每一轮的迭代过程如下:
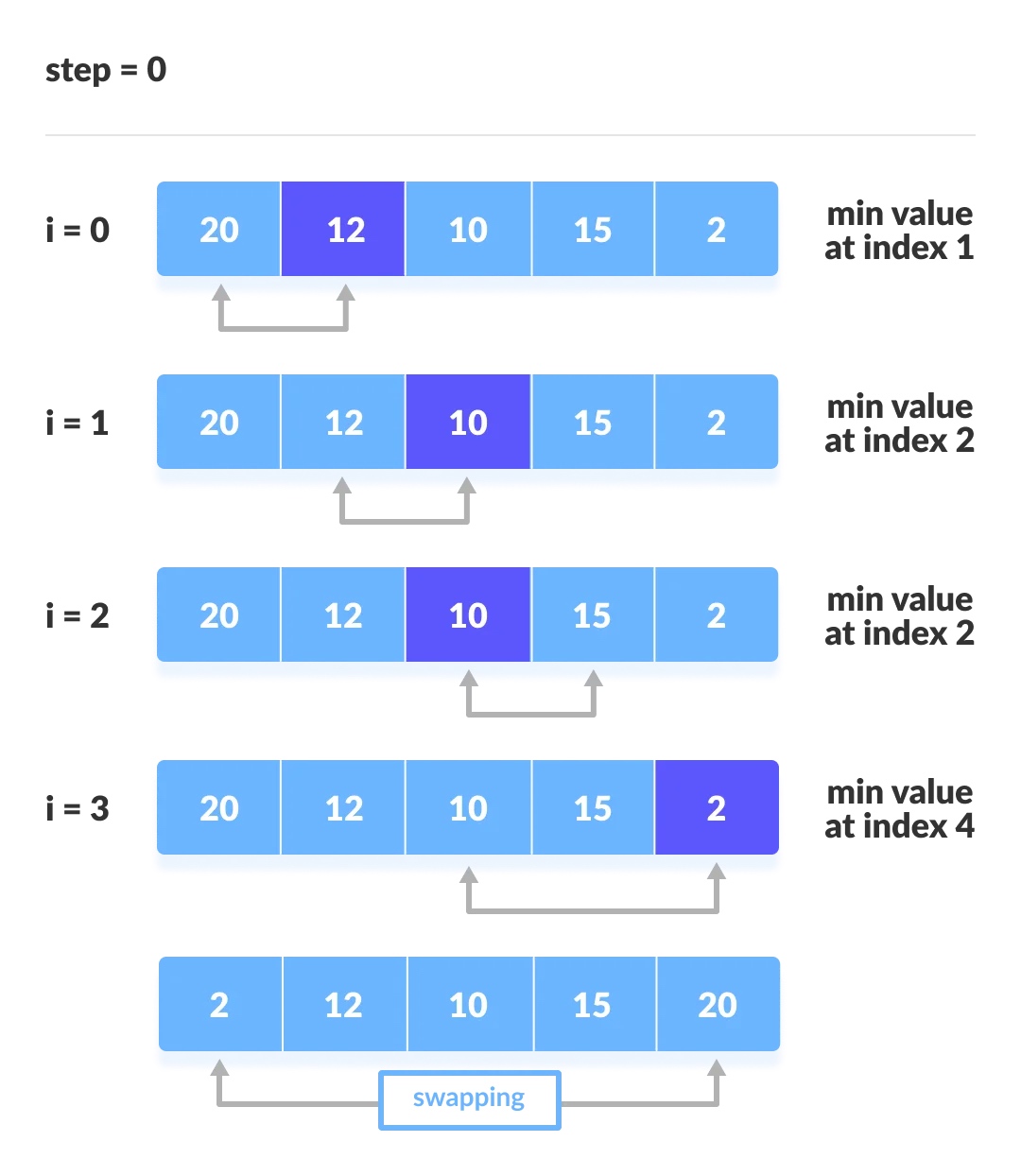
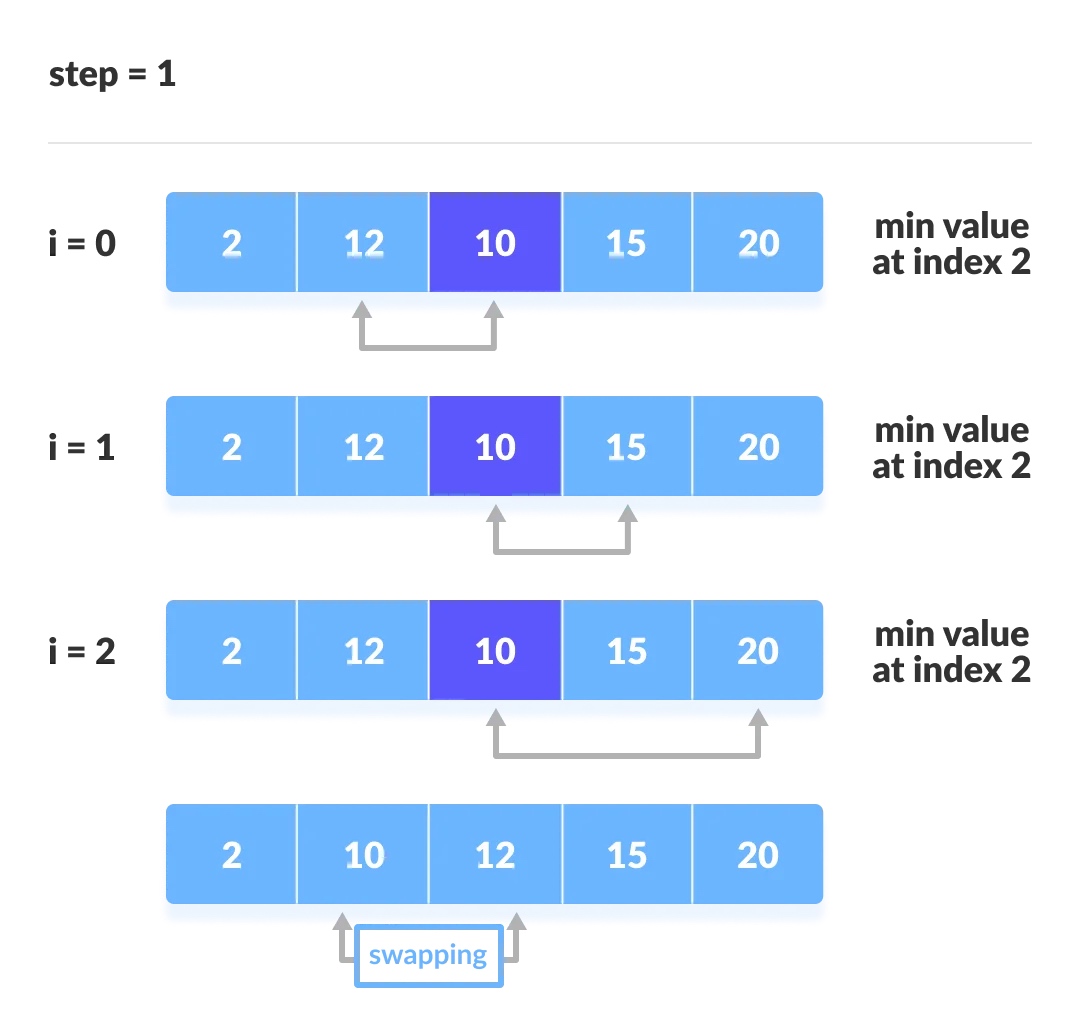
复杂度
|Time Complexity|| |—|—| |Best | O(n^2) | |Worst | O(n^2) | |Average | O(n^2) | |Space Complexity | O(1) | |Stability | No |
代码实现
Swfit实现
import Foundation
func selectSort(array: inout [Int]) {
//遍历array,在每一轮中递增i
for i in 0 ..< array.count - 1 {
var min_idx = i //定义一个最小值
//找出除i以外的列表中的最小值
for j in i+1 ..< array.count {
if array[j] < array[min_idx] { //找到更小的,更新 min_idx
min_idx = j
}
}
//把最小值换到正确的位置,也就是i的位置,之后再进行下一轮迭代
if min_idx != i {
array.swapAt(i, min_idx)
}
}
}
//打印
func printSelectSort(_ array:inout [Int]){
selectSort(array: &array)
print(array)
}
var arr:[Int] = [3, 2, 5, 7, 1, 5, 4, 8, 11, 0]
printSelectSort(&arr)
Python实现
# Selection sort in Python
def selectionSort(array, size):
for step in range(size):
min_idx = step
for i in range(step + 1, size):
# to sort in descending order, change > to < in this line
# select the minimum element in each loop
if array[i] < array[min_idx]:
min_idx = i
# put min at the correct position
(array[step], array[min_idx]) = (array[min_idx], array[step])
data = [-2, 45, 0, 11, -9]
size = len(data)
selectionSort(data, size)
print('Sorted Array in Ascending Order:')
print(data)
Java实现
// Selection sort in Java
import java.util.Arrays;
class SelectionSort {
void selectionSort(int array[]) {
int size = array.length;
for (int step = 0; step < size - 1; step++) {
int min_idx = step;
for (int i = step + 1; i < size; i++) {
// To sort in descending order, change > to < in this line.
// Select the minimum element in each loop.
if (array[i] < array[min_idx]) {
min_idx = i;
}
}
// put min at the correct position
int temp = array[step];
array[step] = array[min_idx];
array[min_idx] = temp;
}
}
// driver code
public static void main(String args[]) {
int[] data = { 20, 12, 10, 15, 2 };
SelectionSort ss = new SelectionSort();
ss.selectionSort(data);
System.out.println("Sorted Array in Ascending Order: ");
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(data));
}
}
C 实现
// Selection sort in C
#include <stdio.h>
// function to swap the the position of two elements
void swap(int *a, int *b) {
int temp = *a;
*a = *b;
*b = temp;
}
void selectionSort(int array[], int size) {
for (int step = 0; step < size - 1; step++) {
int min_idx = step;
for (int i = step + 1; i < size; i++) {
// To sort in descending order, change > to < in this line.
// Select the minimum element in each loop.
if (array[i] < array[min_idx])
min_idx = i;
}
// put min at the correct position
swap(&array[min_idx], &array[step]);
}
}
// function to print an array
void printArray(int array[], int size) {
for (int i = 0; i < size; ++i) {
printf("%d ", array[i]);
}
printf("\n");
}
// driver code
int main() {
int data[] = {20, 12, 10, 15, 2};
int size = sizeof(data) / sizeof(data[0]);
selectionSort(data, size);
printf("Sorted array in Acsending Order:\n");
printArray(data, size);
}
C++ 实现
// Selection sort in C++
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
// function to swap the the position of two elements
void swap(int *a, int *b) {
int temp = *a;
*a = *b;
*b = temp;
}
// function to print an array
void printArray(int array[], int size) {
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {
cout << array[i] << " ";
}
cout << endl;
}
void selectionSort(int array[], int size) {
for (int step = 0; step < size - 1; step++) {
int min_idx = step;
for (int i = step + 1; i < size; i++) {
// To sort in descending order, change > to < in this line.
// Select the minimum element in each loop.
if (array[i] < array[min_idx])
min_idx = i;
}
// put min at the correct position
swap(&array[min_idx], &array[step]);
}
}
// driver code
int main() {
int data[] = {20, 12, 10, 15, 2};
int size = sizeof(data) / sizeof(data[0]);
selectionSort(data, size);
cout << "Sorted array in Acsending Order:\n";
printArray(data, size);
}